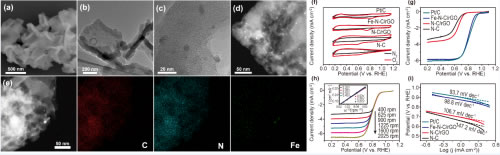
Institute of Solid State Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Solid State Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Preparation and Processing of Iron-nitrogen-doped Porous Carbon/Graphene Composites with Dual Active Sites in Oxygen Reduction Made progress in the related work published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Due to the depletion of fossil energy and the deterioration of the natural environment, people began to vigorously develop sustainable energy storage and conversion systems such as metal-air batteries and fuel cells. However, the kinetics of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) kinetics of these energy conversion and storage devices is slow and often requires the use of a catalyst to increase the activity of the reaction. Studies have found that platinum-based electrocatalysts are currently the better performing catalysts for ORR. However, the precious metal platinum reserves are small, and the price is expensive, which is not conducive to large-scale promotion and application. Therefore, the search for non-precious metal catalysts with excellent performance and good stability is the research direction. Among them, iron-nitrogen/carbon-based electrocatalysts have received more and more attention due to their rich surface metal-nitrogen dual active sites. At present, such catalysts usually need to be synthesized at a high temperature, and tend to cause catalyst agglomeration during the synthesis, thereby reducing the specific surface area of ​​the catalyst and the number of exposed active sites. In response to these problems, researchers used liquid-phase laser ablation technology to create special local and extreme conditions (liquid-solid interface) in a mild environment to first obtain ferrocolloid nanoparticles with high activity and high chemical reactivity. The Fe-NC/rGO electrocatalyst can be uniformly prepared on the surface of graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets by introducing a carbon-nitrogen source and subsequent pyrolysis process (as shown in (a) to (e)). Due to the formation of a sheet-like structure after being compounded with graphene, the agglomeration of the catalyst is effectively avoided, the specific surface area and the exposed active sites of the catalyst are increased, and the catalytic activity of the iron-nitrogen/carbon-based electrocatalyst is further improved. Further electrochemical tests show that it has good electrocatalytic properties (as shown in (f)-(i)), and the Fe-based nanoparticles and Fe-N sites contained in the catalyst have catalytic activity for the catalyst. Significant influence. The research work provides new research ideas for the construction and development of new metal-nitrogen/carbon-based electrocatalysts, and is expected to replace precious metal platinum for fuel cells and metal-air batteries. The research work was funded by the National Key Basic Research Development Program (973 Program), the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Research and Development Equipment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Fe-NC/rGO catalysts: (a) SEM photographs; (b,c) TEM photographs; (d) HAADF-STEM photographs; (e) EDX mapping photographs; (f) Different catalysts in 0.1 M nitrogen or oxygen saturated KOH Cyclic voltammograms of the solution; (g) Linear sweep voltammetry curves of Fe-NC/rGO in oxygen-saturated 0.1 M KOH solution; (h) Difference of Fe-NC/rGO in 0.1 M KOH solution saturated with oxygen Linear sweep voltammograms at speed; (i) Comparison of Tafel curves for different catalysts.
a screw screwed through one part tightly upon or into another part to prevent relative movement
a screw for regulating a valve opening or a spring tension
Set Screws,Allen Set Screw,Socket Set Screw,Stainless Steel Set Screws Taizhou Risco Stainless Steel Products Co.,Ltd , https://www.riscofastener.com