Steel rail The most common form of guide rails on machine tools is steel-inlaid rails, which have a long history of use. The inlaid steel rail is a fixed component of the rail system and has a rectangular cross section. It can be mounted horizontally on the machine bed or integrated into the bed, known as steel or monolithic. The inlaid steel guide rails are made of steel and are hardened and ground. Hardness is more than 60 degrees Rockwell hardness, and the steel guide rail is attached to the machine bed or the scraped column mating surface with screws or adhesive (epoxy resin) to ensure the best flatness of the guide rail. This form is convenient and simple to repair and replace, and is very popular with maintenance workers. The integral rail or the cast rail, that is, the steel rail is integrally molded with the base, and is then ground to the required size and finish after processing. The guide rail must be subjected to flame hardening to increase the surface hardness to improve the wear resistance of the guide rail. The bed is generally ductile iron. Of course, ductile iron is harder than steel. The integral rail can be repaired and hardened, but it is almost impossible to replace it. In order to achieve the above objectives, the conventional practice of the machine tool builder is that the edge of the steel guide rail is designed with a hook-shaped "ear". Before casting the base, the steel guide rail is placed in the mold of the base, and the molten iron is poured into the mold. In this way, the steel rail is integrally molded with the base. Sliding rail The development of conventional guide rails is first manifested in the form of sliding elements and guide rails. The characteristics of the sliding guide rails are that the medium is used between the guide rails and the slide members, and the difference in form is to select different media. Hydraulics are widely used in many rail systems. The hydrostatic guide rail is one of them. The hydraulic oil enters the groove of the sliding member under pressure and forms an oil film between the guide rail and the sliding member to separate the guide rail from the moving member, thereby greatly reducing the frictional force of the moving member. The hydrostatic guide rail is extremely effective for large loads and compensates for eccentric loads. For example, a large sand box is just at the end of the machine stroke when it is being machined. The load rail can increase the oil pressure and keep the rails in a state of horizontal load. Some horizontal boring and milling machines use this technique to compensate for the drop in spindle speed during deep hole machining. Another form of rail that uses oil as a medium is a dynamic pressure rail. The difference between a dynamic pressure rail and a hydrostatic rail is that the oil does not act under pressure. It uses the viscosity of the oil to avoid the movement between the moving element and the rail. The direct contact has the advantage of saving the Hydraulic Pump. Previous page next page Fy Bearing Heater,Cone Bearing Heater,Fag Bearing Heater,Eddytherm Bearing Heater Taizhou Juhuan Lifting Protection Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.jsjoba.com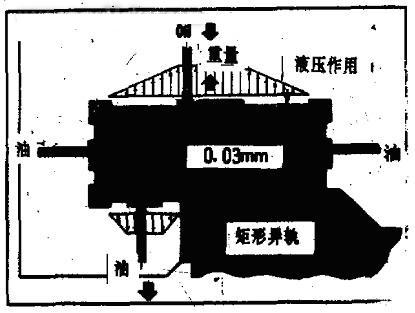
figure 1